Addressing Kenya’s Rising Diabetes Cases: Prevention and Treatment
Introduction
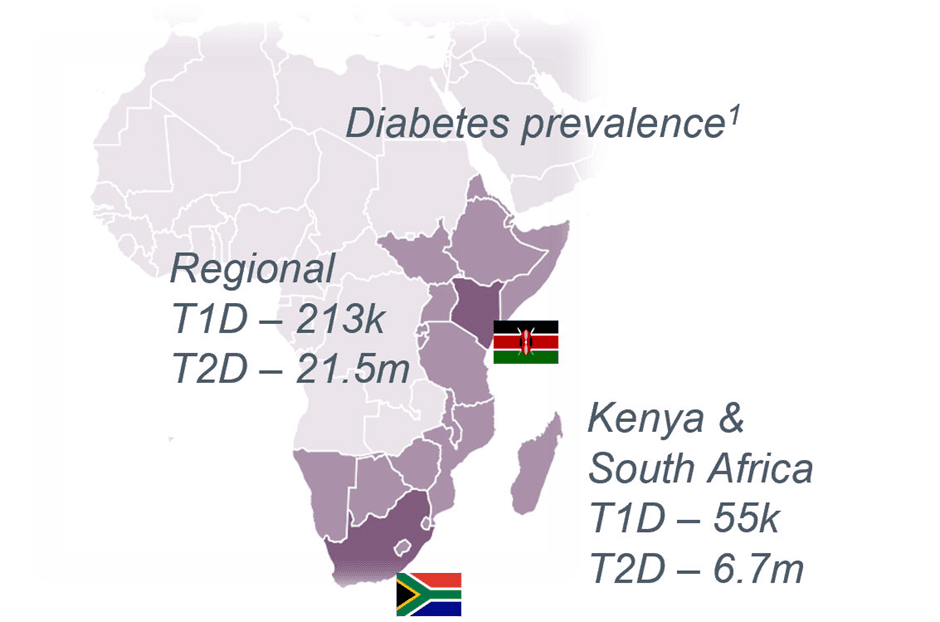
Source: finddx.org
Diabetes is a growing public health concern in Kenya, with the number of cases rising at an alarming rate. According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), approximately 2.5 million Kenyans were living with diabetes in 2021, and this number is projected to increase significantly by 2030. The disease is not only a personal health issue but also a national burden, straining the country’s healthcare system and economy.
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin. It is broadly categorized into Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. Type 2 diabetes, which is largely preventable, accounts for the majority of cases in Kenya. The rise in diabetes cases is attributed to urbanization, sedentary lifestyles, and poor dietary habits. This blog explores the causes, prevention strategies, treatment options, and the impact of diabetes on Kenya’s healthcare system, offering actionable solutions to address this epidemic.
Causes and Risk Factors

Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in the development of diabetes. Individuals with a family history of the disease are at a higher risk of developing it. In Kenya, certain ethnic groups, such as the Luo and Kamba, have shown a higher predisposition to diabetes due to genetic factors.
Lifestyle Factors
Urbanization has led to a shift from traditional, active lifestyles to more sedentary ones. Many Kenyans now work in office settings, reducing physical activity levels. Additionally, the proliferation of motorized transport has decreased walking and cycling, further contributing to physical inactivity.
Dietary Factors
The adoption of Western diets high in refined sugars, unhealthy fats, and processed foods has exacerbated the problem. Traditional Kenyan diets, rich in whole grains, vegetables, and lean proteins, are being replaced by fast food and sugary beverages. This dietary shift has led to an increase in obesity, a major risk factor for Type 2 diabetes.
Socioeconomic Factors
Poverty and lack of access to healthcare services also contribute to the rising diabetes cases. Many Kenyans cannot afford regular medical check-ups or diabetes management tools, such as glucose meters and insulin. Additionally, limited health education means that many people are unaware of the risks and symptoms of diabetes.
Prevention Strategies

Source: Shutterstock
Public Health Initiatives
The Kenyan government, in collaboration with non-governmental organizations (NGOs), has launched several public health initiatives to combat diabetes. These include free screening camps, awareness campaigns, and the integration of diabetes care into primary healthcare services. For example, the Ministry of Health’s National Strategy for the Prevention and Control of Non-Communicable Diseases aims to reduce the prevalence of diabetes through early detection and lifestyle interventions.
Dietary Changes
Promoting healthy eating habits is crucial in preventing diabetes. Public awareness campaigns can educate Kenyans about the benefits of traditional diets and the dangers of processed foods. Schools and workplaces can also play a role by offering healthier meal options and banning sugary drinks.
Physical Activity
Encouraging physical activity is another key prevention strategy. The government can invest in public recreational facilities, such as parks and sports centers, to promote exercise. Community-based programs, such as walking clubs and fitness classes, can also help increase physical activity levels.
Awareness Campaigns
Raising awareness about diabetes is essential for prevention. Media campaigns, workshops, and community outreach programs can educate the public about the risk factors, symptoms, and importance of early detection. Celebrities and influencers can be leveraged to spread the message and encourage healthy lifestyles.
Treatment and Management

Source: WHO
Medical Treatments
Diabetes management in Kenya typically involves a combination of medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring. Common medications include metformin and insulin therapy. However, access to these treatments remains a challenge for many due to high costs and limited availability in rural areas.
Alternative Therapies
In addition to conventional treatments, some Kenyans turn to alternative therapies, such as herbal remedies and acupuncture. While these methods may provide symptomatic relief, they should not replace medical treatment. It is essential for patients to consult healthcare professionals before trying alternative therapies.
Government Interventions
The Kenyan government has taken steps to improve diabetes care, such as subsidizing the cost of insulin and other medications. The National Health Insurance Fund (NHIF) now covers some diabetes-related expenses, making treatment more accessible. However, more needs to be done to ensure that all Kenyans, especially those in rural areas, have access to affordable diabetes care.
Impact on Healthcare System

Source: Shutterstock
Burden on Infrastructure
The rising prevalence of diabetes has placed a significant burden on Kenya’s healthcare system. Hospitals and clinics are often overwhelmed, leading to long wait times and inadequate care. The cost of treating diabetes and its complications, such as kidney failure and cardiovascular disease, is also straining the country’s healthcare budget.
Economic Impact
Diabetes not only affects individuals but also has broader economic implications. The disease reduces productivity due to absenteeism and early retirement, impacting Kenya’s workforce. Additionally, the high cost of treatment often pushes families into poverty, exacerbating socioeconomic inequalities.
Policy Recommendations
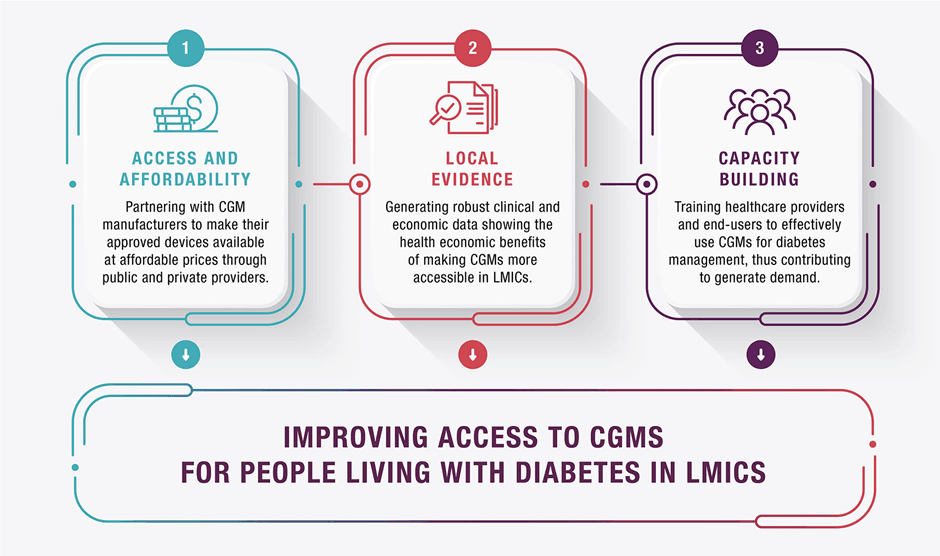
Source: finddx.org
To address these challenges, the Kenyan government should consider the following policy recommendations:
- Increase Funding for Diabetes Care: Allocate more resources to diabetes prevention and treatment programs.
- Expand Healthcare Access: Build more healthcare facilities in rural areas and train healthcare workers to manage diabetes.
- Promote Public-Private Partnerships: Collaborate with private sector stakeholders to improve access to affordable diabetes medications and technologies.
- Implement Sugar Taxes: Introduce taxes on sugary beverages and processed foods to discourage their consumption and generate revenue for diabetes programs.
Conclusion
Kenya’s rising diabetes cases are a pressing public health issue that requires urgent attention. The disease is driven by a combination of genetic, lifestyle, and socioeconomic factors, making it a complex challenge to address. However, through targeted prevention strategies, improved treatment options, and robust government interventions, it is possible to curb the diabetes epidemic.
Public health initiatives, dietary changes, and increased physical activity are essential for prevention. At the same time, expanding access to affordable healthcare and raising awareness about diabetes can improve management outcomes. By addressing the burden on the healthcare system and implementing effective policies, Kenya can reduce the impact of diabetes on its population and economy.
The fight against diabetes requires a collective effort from the government, healthcare providers, communities, and individuals. With sustained commitment and action, Kenya can turn the tide on this growing epidemic and ensure a healthier future for all.
Reference link:
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF) – Diabetes Atlas: https://www.diabetesatlas.org
- Kenyan Ministry of Health – Non-Communicable Diseases Strategy: https://www.health.go.ke
- World Health Organization (WHO) – Global Report on Diabetes: https://www.who.int/diabetes/global-report/en/
- Kenya Demographic and Health Survey (KDHS) 2020 Report: https://dhsprogram.com/pubs/pdf/FR308/FR308.pdf
- National Health Insurance Fund (NHIF) – Diabetes Coverage: https://www.nhif.or.ke
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) – Diabetes Prevention
https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/prevention/index.html - American Diabetes Association – Diabetes Care: https://www.diabetes.org
- Kenya National Bureau of Statistics (KNBS) – Health Statistics: https://www.knbs.or.ke






