Kenya’s Tea and Coffee Industry: Can It Compete Globally?

Source: Shutterstock
Kenya’s tea and coffee industries have long been vital pillars of its economy, contributing significantly to foreign exchange earnings and employment. The country’s tea, renowned for its strong flavor and rich aroma, is among the best globally, while Kenyan coffee enjoys a premium status in specialty markets. However, as international competition intensifies, Kenya must navigate various challenges and opportunities to sustain and expand its market share.
Kenya’s Tea and Coffee Industry: An Overview


Source: iStock
Tea Industry
Kenya is among the top tea-producing nations, focusing primarily on black tea. The industry employs over 650,000 small-scale farmers and contributes significantly to the country’s GDP.
- Production: In 2023, Kenya produced approximately 540,000 metric tonnes of tea.
- Exports: Kenya exported about 95% of its tea to international markets, with key buyers including Pakistan, Egypt, and the United Kingdom.
- Earnings: Tea exports generated around USD 1.3 billion in revenue in 2023.
Despite these impressive numbers, Kenya’s tea sector faces stiff competition from India, Sri Lanka, and China, which offer a broader variety of teas, including green and white teas.
Coffee Industry
Kenyan coffee is highly valued in specialty coffee markets due to its bright acidity and full-bodied flavor. However, the industry has struggled with declining production and fluctuating global prices.
- Production: Kenya produced approximately 50,000 metric tonnes of coffee in 2023.
- Exports: Over 95% of Kenya’s coffee is exported, with primary markets in the United States, Germany, and Belgium.
- Earnings: Kenya’s coffee export earnings have fluctuated, but in December 2024, coffee revenues soared even as tea earnings declined by 20%.
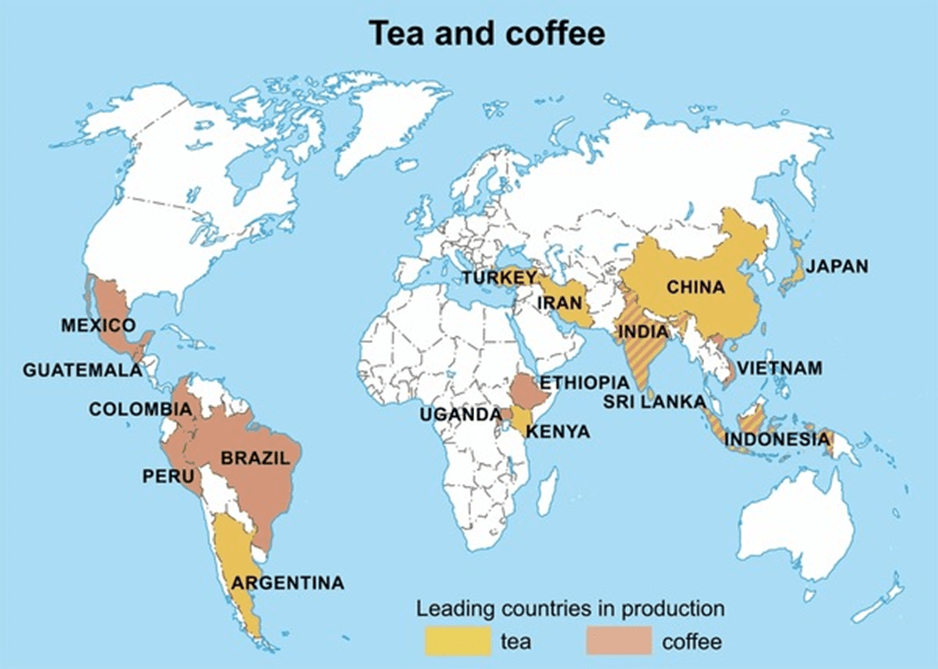
How Kenya Compares to Global Competitors
Source: Shutterstock


Tea Market
Kenya’s tea industry competes with:
- India: The world’s second-largest tea producer, offering a diverse range, including Assam, Darjeeling, and Nilgiri teas.
- Sri Lanka: Famed for its premium Ceylon tea, marketed aggressively worldwide.
- China: Dominates in green tea and specialty teas with advanced processing technologies.
Despite Kenya’s leadership in black tea production, its limited variety and heavy reliance on bulk exports put it at a disadvantage.
Coffee Market
In the coffee sector, Kenya faces stiff competition from:
- Brazil: The largest coffee producer, accounting for nearly 40% of global coffee supply.
- Vietnam: A major exporter of robusta coffee, known for its cost-effective production.
- Colombia: A strong player in the arabica segment with a well-established global brand.
Although Kenya’s coffee is prized for quality, its overall production volume remains low compared to these giants.
Strengths of Kenya’s Tea and Coffee Industry
Source: Adobe Stock & Shutterstock
1. Superior Quality and Unique Flavor
Kenyan tea and coffee are highly regarded for their strong flavors, thanks to the country’s rich volcanic soils and favorable climatic conditions. Kenyan tea is primarily processed using the Cut, Tear, and Curl (CTC) method, producing high-quality black tea with a robust taste.
2. Sustainable Farming Practices
Kenya has been adopting sustainable agricultural practices, such as climate-smart farming and carbon credit initiatives, making its tea and coffee more attractive to environmentally conscious consumers.
3. Strong Export Markets
Kenyan tea and coffee have well-established markets, particularly in Europe, the Middle East, and North America, with increasing demand for high-quality products.
Challenges Facing Kenya’s Tea and Coffee Industry

Source: Fresh Cup Magazine
1. Pricing and Market Access
- Tea: Despite high production, Kenya’s tea export earnings declined by 20% in December 2024, signaling pricing pressures.
- Coffee: Declining farm-gate prices discourage farmers, leading to reduced production.
2. Climate Change
Erratic weather patterns, prolonged droughts, and unpredictable rainfall affect yields, threatening the sustainability of both tea and coffee farming.


3. Weak Branding and Value Addition
Unlike Colombia’s “Café de Colombia” branding strategy, Kenya’s tea and coffee are mostly exported in bulk rather than as premium branded products, reducing their value in the global market.
4. Policy and Regulatory Constraints
There have been concerns over inefficient regulatory frameworks, high taxation, and delayed farmer payments, discouraging investment and growth in the sector.
Opportunities for Kenya to Enhance Competitiveness
Source: Freepik
1. Value Addition
Investing in processing and packaging facilities to produce branded specialty teas and coffees can help Kenya command higher prices and expand into premium markets.
2. Geographic Indication and Branding
Securing geographic indication (GI) status for Kenyan tea and coffee, similar to Champagne for French wine, can boost global recognition and demand.
3. Technological Advancements
Utilizing agriculture technology (AgriTech) such as smart irrigation, AI-driven weather forecasting, and blockchain for traceability can enhance productivity and attract premium buyers.
4. Expansion into Emerging Markets
Kenya should explore new markets in Asia, North America, and the Middle East, diversifying beyond traditional buyers.
5. Government Policies and Support
The government should streamline tax policies, improve infrastructure, and offer subsidies to encourage increased production and fair pricing.
Conclusion
Kenya’s tea and coffee industries remain globally competitive due to their high quality and rich heritage. However, addressing challenges such as pricing, branding, and climate change is crucial for sustainable growth. By investing in value addition, embracing technology, and expanding market reach, Kenya can solidify its position as a dominant player in the global tea and coffee trade.
Reference Links:
Tea Board of Kenya – https://www.teaboard.or.ke
Kenyan Coffee Exchange – https://www.nce.co.ke
Kenyan Tea & Coffee Market Trends – https://www.selinawamucii.com
Climate Adaptation Initiatives – https://www.kepsa.or.ke