How Wearable Technology is Enhancing Healthcare in Kenya in 2025
Introduction
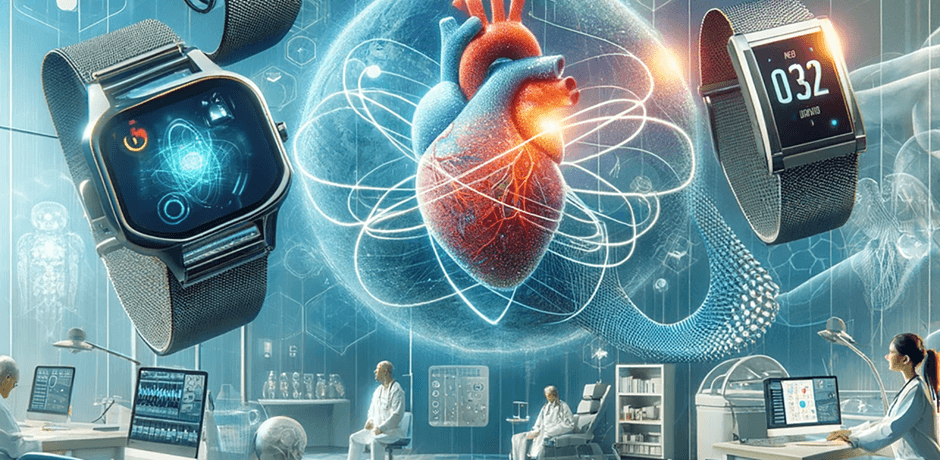
Wearable technology has become a transformative force in the healthcare sector globally, and Kenya is no exception. As the country grapples with various health challenges, such as communicable diseases, maternal health issues, and chronic conditions, wearable technology is providing a new avenue for improving healthcare delivery. These innovative devices, which can monitor health parameters in real-time, empower both patients and healthcare providers to make informed decisions, leading to better outcomes.
In 2025, wearable tech has advanced significantly, with more sophisticated devices designed to track vital signs, manage chronic diseases, and even facilitate telemedicine. This blog will explore how wearable technology is revolutionizing healthcare in Kenya, the benefits it offers, and the challenges to widespread adoption, while also looking at its potential future role in the country’s healthcare landscape.
The Role of Wearable Technology in Healthcare

Wearable devices such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and health-monitoring gadgets are no longer just for fitness enthusiasts. In Kenya, these devices are gaining popularity among both urban and rural populations, playing a crucial role in the prevention, diagnosis, and management of various health conditions. Here’s how wearable technology is improving healthcare in Kenya:
- Chronic Disease Management
Chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, and heart disease are on the rise in Kenya, driven by factors such as urbanization, dietary changes, and lifestyle habits. Wearables equipped with heart rate monitors, blood glucose sensors, and blood pressure tracking capabilities allow individuals to manage their conditions proactively.
Devices such as the Fitbit Charge or Apple Watch now include ECG functionality (electrocardiogram), allowing users to monitor their heart health at any time. For Kenyan patients with chronic conditions, these wearables provide real-time data, enabling them to make immediate adjustments to their treatment regimens. Doctors can also access this data remotely, improving the quality of care and reducing the need for frequent visits to health facilities. - Remote Patient Monitoring and Telemedicine
The shortage of healthcare professionals and facilities in rural areas of Kenya has long been a challenge. However, wearable technology is helping bridge this gap. Through remote patient monitoring, wearables enable healthcare providers to track the health status of patients from a distance. For instance, smartwatches can collect data such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and even oxygen levels, transmitting this information directly to doctors via cloud-based platforms.
Telemedicine services in Kenya, supported by wearables, are empowering healthcare providers to conduct virtual consultations, offering advice and guidance based on the real-time data sent by wearable devices. This has proven invaluable for patients living in rural regions, where access to healthcare facilities is limited. - Preventive Healthcare and Early Detection
Wearables play a significant role in preventive healthcare, helping individuals track their physical activity, diet, and other habits that influence long-term health. For instance, smart fitness trackers can motivate users to stay active, helping prevent lifestyle-related diseases such as obesity and cardiovascular issues.
In addition to general fitness tracking, wearables are capable of early detection of potential health issues. Some devices, like the Oura Ring and Whoop Strap, track users’ sleep quality and monitor for abnormal sleep patterns that could indicate underlying health problems like sleep apnea or stress. In Kenya, where resources for early detection may be limited, wearables offer a promising solution to catch potential health problems early, before they escalate into more serious conditions. - Maternal and Child Health
Maternal health remains a significant challenge in Kenya, with high rates of maternal mortality and infant deaths. Wearable technology is playing an increasing role in improving maternal care. Devices such as the Bellabeat Leaf are designed specifically for pregnant women, offering features like fetal monitoring and tracking of important physiological indicators such as heart rate and stress levels. These devices help expecting mothers monitor their health, reducing the likelihood of complications during pregnancy.
Wearables can also aid in post-natal care by tracking the health of newborns. In Kenya, wearable devices that monitor infant vitals such as temperature and oxygen levels are helping caregivers detect signs of distress early, which is crucial for saving lives.
Benefits of Wearable Technology in Healthcare
- Accessibility and Convenience
One of the primary benefits of wearable devices in healthcare is their accessibility and convenience. Unlike traditional medical equipment, which often requires a visit to a healthcare facility, wearables allow users to monitor their health from the comfort of their homes or on the go. For many Kenyans, especially those in rural areas, this is an opportunity to access healthcare services without the need for expensive or distant hospital visits. - Real-Time Data and Improved Decision Making
Wearable devices offer continuous monitoring and provide real-time data. This allows for timely interventions, especially in emergency situations. For example, if a patient’s heart rate becomes irregular, the wearable can send an alert to the user and their healthcare provider, prompting immediate action. This level of responsiveness can prevent complications and even save lives. - Cost-Effective Healthcare Solutions
The ability of wearables to offer continuous, real-time health monitoring can reduce the need for frequent hospital visits or expensive diagnostic procedures. In Kenya, where healthcare costs can be a significant barrier for many, wearables provide a more affordable alternative for patients to manage chronic conditions and maintain good health.
Challenges to Overcome in Kenya

Despite their potential, there are several challenges to the widespread adoption of wearable technology in Kenya’s healthcare system:
- Cost of Wearables
While prices for wearables have been steadily decreasing, the initial cost of purchasing these devices can still be prohibitive for many Kenyans. The challenge lies in making these technologies more affordable and accessible to a broader population. Financial barriers need to be addressed, especially for those in lower-income brackets. - Limited Internet Connectivity in Rural Areas
The effectiveness of wearables often depends on the ability to transmit data to healthcare providers or cloud-based platforms. In rural parts of Kenya, internet connectivity remains a challenge, which can hinder the functionality of these devices. Increased investment in internet infrastructure and mobile networks is essential to ensure that wearables can be used effectively across the country. - Health Literacy
While wearables are easy to use, understanding how to interpret the data they provide can be a challenge for some users. There is a need for education around how to use wearable devices and understand their readings, particularly in rural areas where health literacy may be lower. Healthcare providers must play a key role in training users and ensuring that they can make the most of their wearable devices.
The Future of Wearable Technology in Kenya’s Healthcare System
Looking ahead, wearable technology has the potential to completely transform healthcare in Kenya. By 2025, we expect to see greater integration of wearables into national health initiatives, particularly in the fields of chronic disease management and maternal health. The government, private sector, and healthcare providers must work together to address challenges related to affordability, internet access, and education to ensure that these technologies reach all Kenyans.
Conclusion
Wearable technology is increasingly becoming an essential tool for enhancing healthcare delivery in Kenya. By enabling continuous monitoring, improving accessibility to health services, and empowering individuals to take control of their health, wearables are playing a crucial role in the country’s health ecosystem. In 2025, as technology continues to evolve, wearables will likely become even more integrated into Kenya’s healthcare system, offering more affordable, efficient, and personalized healthcare solutions.
References