The Role of Robotics in Kenya’s Manufacturing Industry in 2025
Introduction
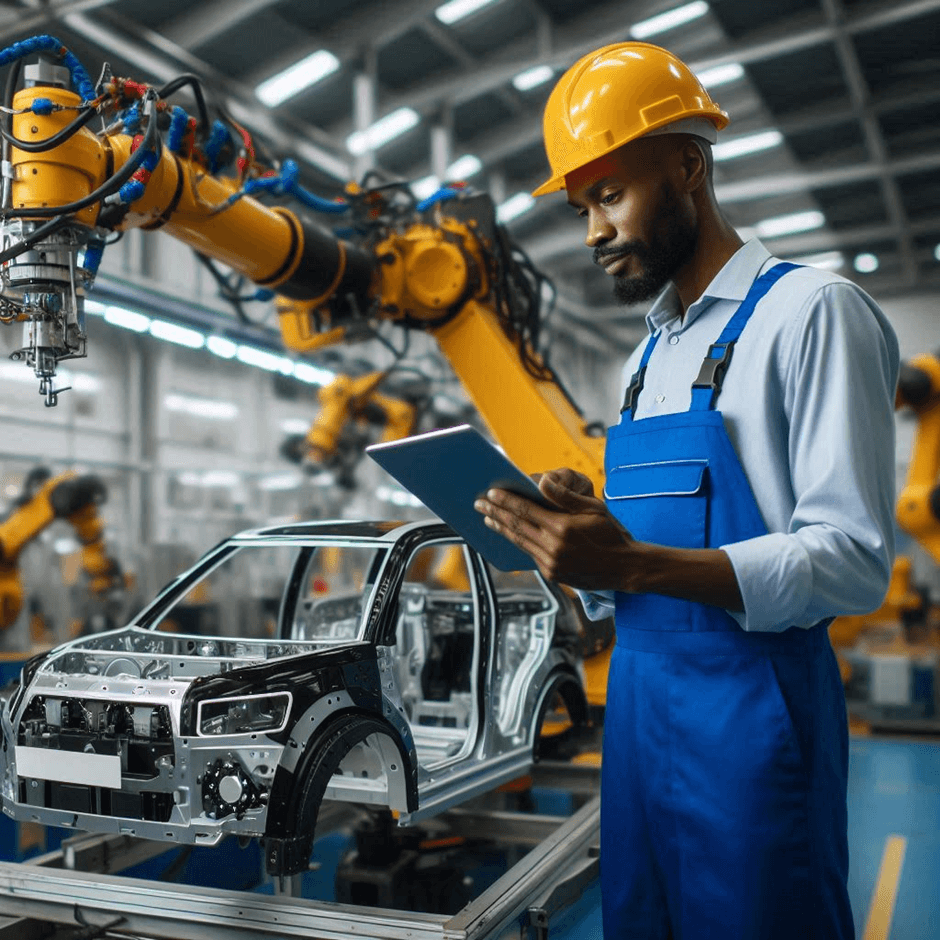
Kenya’s manufacturing industry is on the cusp of a technological transformation. Robotics, once a distant dream, is now becoming a cornerstone of modern manufacturing processes. From automating assembly lines to enhancing quality control, robotics is enabling Kenyan manufacturers to achieve greater efficiency, precision, and cost-effectiveness.
As Kenya aspires to position itself as a regional manufacturing hub, the integration of robotics could accelerate its journey. In this blog, we delve into how robotics is shaping Kenya’s manufacturing landscape, its benefits, and the challenges that need to be addressed in 2025.
The Current Landscape of Robotics in Kenya

Kenya’s manufacturing sector, contributing about 7.5% to GDP, is undergoing significant modernization. Robotics is playing a pivotal role in this transformation.
- Streamlining Production Processes
Robotic systems are being used to automate repetitive tasks like assembly, packaging, and welding. This reduces errors and boosts productivity. - Enhanced Quality Assurance
Robotics integrated with AI is enabling real-time quality checks, ensuring higher product standards while minimizing waste. - Empowering SMEs
Affordable robotic solutions are empowering small and medium enterprises (SMEs) to optimize production and compete with larger firms.
Key Benefits of Robotics in Manufacturing

- Higher Productivity Levels
Robots can work continuously without fatigue, significantly increasing production capacity. - Safer Work Environments
Dangerous tasks such as handling chemicals or heavy machinery are being assigned to robots, reducing workplace accidents. - Cost-Effective Operations
Despite the high initial investment, the operational cost savings from robotics justify the expenditure over time.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Cost Barriers
The initial cost of acquiring and deploying robotics is a major challenge for many manufacturers. However, partnerships and government subsidies could mitigate this. - Skill Shortages
Operating and maintaining robotic systems requires skilled personnel. Training initiatives are crucial to bridge this gap. - Public Concerns About Job Losses
Automation might lead to fears of job displacement. Upskilling workers for advanced roles will be key to ensuring a balanced transition.
What to Expect in 2025

By 2025, robotics in Kenyan manufacturing is expected to gain widespread adoption across industries such as automotive, food processing, and textiles. Collaborative robots (cobots), which work alongside humans, are likely to become the norm. Furthermore, Kenyan tech startups are expected to develop cost-effective robotic solutions tailored to local needs, driving further innovation in the sector.
Conclusion
The role of robotics in Kenya’s manufacturing industry is pivotal for achieving industrial growth and global competitiveness. While challenges such as high costs and skill gaps exist, targeted efforts can unlock the full potential of robotics. With advancements in technology and collaborative efforts among stakeholders, Kenya is poised to leverage robotics to transform its manufacturing industry by 2025.
References