Using Predictive Analytics to Address Kenya’s Urban Challenges in 2025
Introduction

Urbanization in Kenya has been rapidly accelerating in recent years, with cities like Nairobi, Mombasa, and Kisumu becoming increasingly crowded. As Kenya’s population continues to grow and urban areas expand, cities face a range of challenges, including traffic congestion, waste management, water supply, and affordable housing. Traditional methods of addressing these urban challenges are often insufficient due to the complexity and scale of the issues.
In 2025, predictive analytics—the use of data, statistical algorithms, and machine learning techniques to forecast future outcomes—has emerged as a powerful tool in addressing urban challenges. By leveraging vast amounts of data, cities can better understand trends and make more informed decisions that improve the quality of life for residents. In this blog, we will explore how predictive analytics is being used to address urban challenges in Kenya, its potential benefits, and the steps needed for its widespread adoption.
Predictive Analytics for Traffic Management
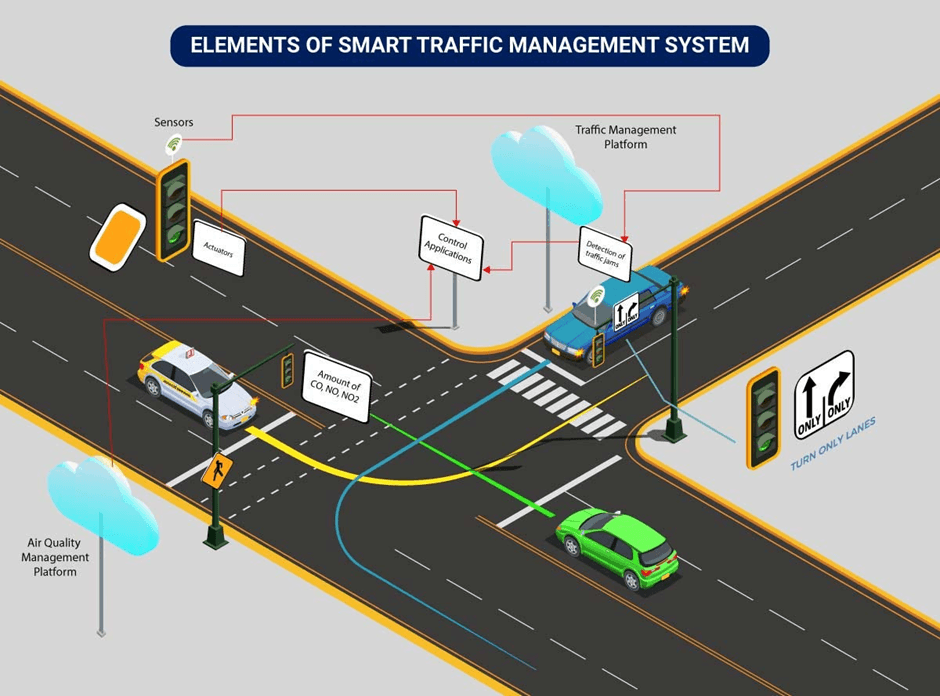
Traffic congestion is one of the most pressing issues in Kenya’s urban areas, particularly in Nairobi. The country’s road network is often overwhelmed by the increasing number of vehicles, resulting in long delays, environmental pollution, and reduced productivity. Predictive analytics is playing a pivotal role in improving traffic flow and reducing congestion.
- Traffic Prediction Models
By analyzing historical traffic data, weather patterns, time of day, and special events, predictive analytics can generate traffic prediction models that forecast traffic conditions in real-time. These models help traffic management authorities in Nairobi, for example, to adjust traffic lights, optimize routing, and inform the public about potential delays.
In 2025, smart traffic systems powered by predictive analytics have been implemented in Nairobi and other cities to proactively manage congestion. For example, systems can identify congestion hotspots and reroute traffic to alternative routes, reducing overall travel time and improving the efficiency of public transportation. - Public Transport Optimization
Predictive analytics is also enhancing public transport systems in Kenya. By analyzing travel patterns and passenger behavior, transport authorities can predict demand for buses and matatus (shared taxis) and adjust schedules accordingly. This leads to better coordination and more efficient service, reducing overcrowding and wait times for commuters.
Predictive Analytics for Waste Management
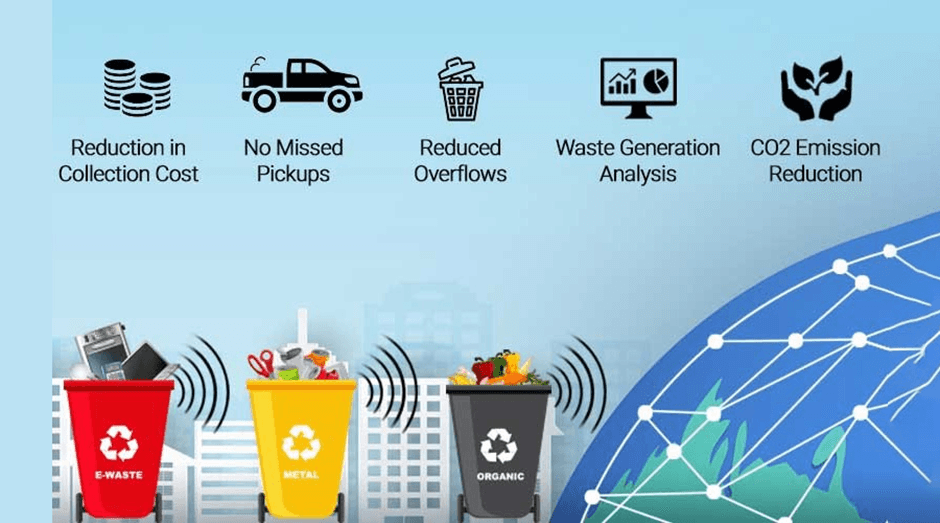
As urban populations grow, effective waste management becomes increasingly challenging. In many Kenyan cities, waste collection and disposal are often irregular, leading to unsightly dumpsites, environmental pollution, and health hazards. Predictive analytics is helping to optimize waste management systems in urban areas.
- Waste Generation Forecasting
By collecting data from households, businesses, and industrial areas, predictive models can forecast the volume of waste generated in specific regions. This allows waste management companies to schedule collections more efficiently and allocate resources where they are needed most. For instance, smart bins equipped with sensors can notify collection teams when they are full, improving operational efficiency. - Recycling and Waste Diversion
Predictive analytics also helps identify opportunities for waste diversion and recycling by forecasting which materials are most likely to be recycled. This helps in planning the sorting and recycling processes, ensuring that recyclable materials are efficiently processed and reducing the burden on landfills.
Predictive Analytics for Urban Planning and Infrastructure

Urban planning in Kenya’s rapidly growing cities often faces challenges due to the lack of accurate data and long-term forecasting. Predictive analytics is increasingly being used to enhance urban planning and guide infrastructure development.
- Urban Growth and Zoning
By analyzing trends in population growth, land use, and infrastructure development, predictive models can help urban planners in Kenya forecast where future growth is likely to occur. This allows for more strategic zoning decisions, helping cities plan for the expansion of roads, utilities, and public services before areas become overcrowded. - Energy and Water Demand Forecasting
With the growth of urban populations, the demand for energy and water is increasing. Predictive analytics can help utilities in Kenyan cities better forecast future demand, optimize distribution, and avoid shortages. For example, by analyzing patterns of water consumption, predictive models can forecast peak demand periods and help municipalities plan for water storage and distribution accordingly. - Building and Infrastructure Maintenance
Predictive analytics can also be applied to predict the lifespan of infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and buildings. By monitoring wear and tear data, cities can forecast when maintenance is needed and prevent costly repairs due to neglected infrastructure.
Predictive Analytics for Housing and Real Estate
Kenya is facing a significant housing shortage, particularly in urban areas. With millions of people moving to cities every year, there is a growing need for affordable housing solutions. Predictive analytics can play a key role in shaping housing policies and helping developers meet the demand for housing.
- Demand Forecasting
By analyzing trends in population growth, income levels, and migration patterns, predictive analytics can help real estate developers forecast the demand for housing in specific areas. This enables developers to build properties in the right locations and at the right time, reducing the risk of overbuilding or underbuilding. - Affordability Predictions
Predictive models can also forecast future trends in housing prices and rental rates. This can help developers and policymakers identify areas where housing is likely to become more affordable or expensive, allowing for better planning of affordable housing initiatives.
Benefits of Predictive Analytics for Urban Challenges
- Improved Decision Making
Predictive analytics provides cities with valuable insights, helping leaders make informed decisions based on real-time data rather than relying on outdated information or guesswork. This enables cities to anticipate issues and act proactively, rather than reacting to problems once they have escalated. - Cost Efficiency
By using predictive models to optimize resource allocation, cities can save money. For example, more efficient traffic management can reduce the need for costly infrastructure projects, and better waste collection systems can reduce operational costs. - Enhanced Quality of Life
Predictive analytics can improve the daily lives of residents by optimizing traffic flow, reducing waste, and improving access to essential services like water and electricity. This enhances the overall quality of life for urban dwellers in Kenya’s rapidly growing cities.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Data Availability and Quality
The effectiveness of predictive analytics depends on the availability and quality of data. In many Kenyan cities, data collection systems are underdeveloped, and the data that is available may be incomplete or inaccurate. Efforts must be made to improve data collection and ensure that predictive models have access to reliable, up-to-date information. - Capacity Building
For predictive analytics to be fully adopted in Kenya, there is a need for capacity building in data science and analytics. Government agencies, municipalities, and businesses will need to invest in training skilled professionals who can develop and implement predictive models. - Privacy and Security Concerns
The use of big data and predictive analytics raises concerns about privacy and data security. Governments and organizations must implement appropriate regulations and safeguards to protect the personal data of citizens.
Conclusion
Predictive analytics is proving to be a game changer in addressing Kenya’s urban challenges. By harnessing the power of data, cities can better manage traffic, waste, infrastructure, and housing. While challenges exist, such as data availability and capacity building, the potential benefits of predictive analytics—improved decision-making, cost efficiency, and enhanced quality of life—make it an invaluable tool for urban development in Kenya. As the technology continues to evolve, it will play an increasingly important role in shaping the future of Kenyan cities.
References








