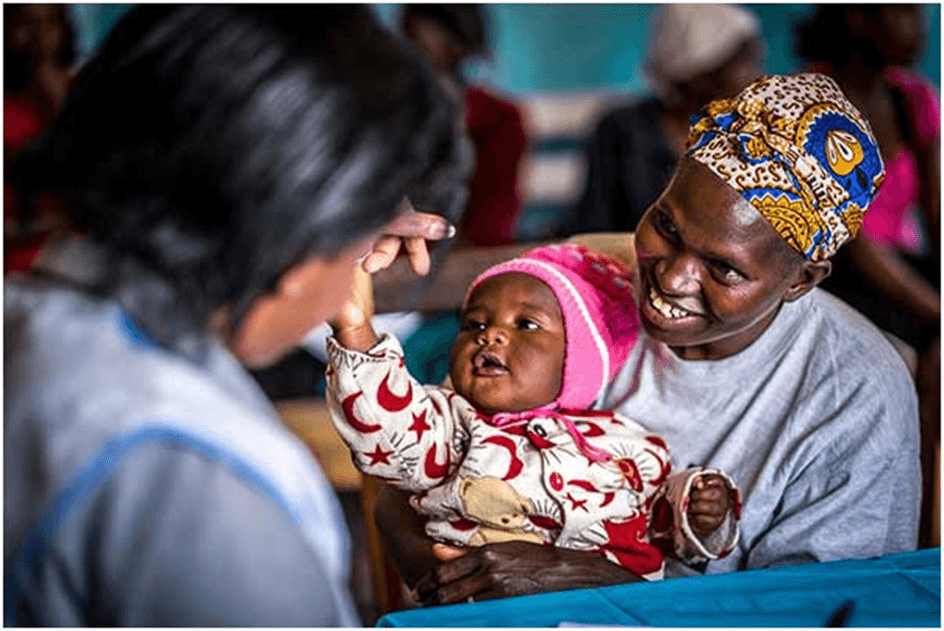
Affordable Healthcare Solutions for Low-Income Kenyan Families
Introduction
In Kenya, the healthcare sector faces significant challenges in delivering affordable and accessible medical services, especially for low-income families. A large proportion of the population struggles with the financial burden of healthcare, which is exacerbated by the limited availability of quality services in rural and underserved areas. However, several innovative solutions are emerging, aimed at improving healthcare access for vulnerable populations while addressing the financial barriers that hinder proper medical care.
This blog explores some of the affordable healthcare solutions that are helping to address these challenges and improve the well-being of low-income Kenyan families. From government initiatives to private sector innovations and community-driven efforts, the healthcare landscape in Kenya is evolving to provide more inclusive and cost-effective care.
Challenges Facing Low-Income Families in Accessing Healthcare
Before delving into the solutions, it is important to understand the specific challenges faced by low-income Kenyan families when accessing healthcare:
1. High Out-of-Pocket Costs
One of the most significant barriers to healthcare access for low-income families is the high cost of medical services. Even with health insurance schemes like NHIF (National Hospital Insurance Fund), many people in informal sectors or rural areas are unable to afford the premiums, leading to inadequate or delayed medical care.
2. Limited Access to Health Facilities
In rural areas, health facilities are often scarce, and those that exist are understaffed and under-resourced. Families living in remote areas may need to travel long distances to access the nearest health facility, which can be a financial and logistical burden.
3. Inadequate Health Insurance Coverage
While NHIF provides health insurance coverage for Kenyan citizens, it often does not cover the full range of healthcare services, particularly for low-income earners. Additionally, a large proportion of the population works in the informal sector and may not be enrolled in NHIF, leaving them without any formal health insurance.
Affordable Healthcare Solutions for Low-Income Kenyan Families

1. Community Health Programs
Community-based healthcare programs are a vital part of the healthcare delivery system in Kenya. These programs are designed to bring health services directly to communities, especially in remote areas where healthcare infrastructure is lacking.
a) Mobile Health Clinics
Mobile health clinics are one of the most effective ways to provide healthcare to underserved populations. These clinics travel to rural areas, offering a wide range of medical services, including consultations, immunizations, maternal care, and disease screenings. By reducing the need for long travel times, mobile clinics make healthcare more accessible to families that would otherwise be unable to visit a hospital.
b) Community Health Workers (CHWs)
CHWs are community-based individuals who are trained to provide basic healthcare services, health education, and support to families in rural or informal settlements. They serve as a bridge between the formal healthcare system and the community, ensuring that essential healthcare services reach the most vulnerable populations. Through these workers, families can receive regular checkups, referrals to health centers, and guidance on how to prevent and manage common illnesses.
2. Affordable Health Insurance Schemes
Health insurance plays a critical role in making healthcare more affordable and accessible. In Kenya, various insurance schemes have been developed to help low-income families access quality care without being overwhelmed by out-of-pocket expenses.
a) National Hospital Insurance Fund (NHIF)
NHIF has been a cornerstone of Kenya’s efforts to provide affordable healthcare to its citizens. In recent years, the government has made strides in expanding NHIF coverage to include informal sector workers, such as farmers, casual laborers, and small business owners. The scheme offers a more affordable alternative to private health insurance and covers a broad range of medical services, including inpatient and outpatient care, maternity, surgery, and even certain specialist treatments.
b) Private Health Insurance for Low-Income Families
In addition to the NHIF, several private insurance companies have begun to tailor affordable health insurance plans specifically designed for low-income families. These plans are typically offered at lower premiums and cover a wide range of essential health services. Some companies also provide group insurance policies for communities or local businesses, making it easier for families to pool resources and afford coverage.
3. Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
Public-private partnerships (PPPs) are becoming increasingly common in Kenya’s healthcare sector, offering collaborative solutions to healthcare access and affordability.
a) Innovative Healthcare Delivery Models
Through PPPs, private health providers partner with the government to offer healthcare services in public facilities. This collaboration allows for the provision of high-quality services at a reduced cost. In some instances, private companies help to improve infrastructure, provide medical equipment, and train staff, all of which contribute to better healthcare delivery for low-income families.
b) Subsidized Health Services
Some private healthcare providers, in partnership with the government, have developed subsidized health services to cater to low-income families. These services may include discounted rates for consultations, medications, and diagnostic tests. Such partnerships ensure that high-quality care is available to families who might otherwise be excluded from the healthcare system due to financial constraints.
4. Telemedicine and Digital Health Solutions

Telemedicine and digital health platforms are revolutionizing healthcare delivery by making medical consultations and health services accessible remotely, especially to rural and underserved communities.
a) Telemedicine Platforms
Telemedicine allows patients to consult with healthcare professionals via phone calls, video conferencing, or chat platforms. This technology has proven invaluable in reducing the barriers of distance, time, and cost that prevent low-income families from accessing healthcare services. Patients can receive medical advice, prescriptions, and follow-up care without having to travel long distances to health facilities.
b) Digital Health Apps
Several mobile health applications have been developed in Kenya to help families manage their healthcare needs. These apps provide information on health topics, allow users to book doctor appointments, receive medication reminders, and access health services at discounted rates. Additionally, some apps offer digital consultations for a variety of health concerns, making healthcare more affordable and accessible.
5. Health Financing Innovations
Apart from insurance, other financing models are emerging to help low-income families afford healthcare.
a) Health Savings Programs
Some microfinance institutions and community-based organizations are offering health savings programs to low-income families. These programs allow families to set aside small amounts of money regularly in a health savings account, which they can use for medical expenses when needed. Such initiatives encourage families to save for healthcare costs while also improving financial literacy.
b) Crowdfunding and Social Enterprises
In cases of serious illnesses that require expensive treatments, some low-income families turn to crowdfunding platforms for support. These platforms allow individuals and communities to raise funds for medical care, often with the help of social media campaigns. Additionally, social enterprises in Kenya are offering innovative financing solutions for healthcare, such as paying for medical treatment in installments or offering reduced-rate healthcare services for families in need.
Conclusion
Affordable healthcare remains a significant challenge for many low-income families in Kenya. However, through innovative solutions such as community health programs, affordable insurance schemes, public-private partnerships, digital health platforms, and health financing models, Kenya is taking important steps toward providing more accessible and affordable medical care for its citizens.
While there is still much work to be done, the healthcare landscape is slowly evolving to better meet the needs of vulnerable populations. By continuing to innovate and invest in these solutions, Kenya has the potential to significantly improve the health outcomes of its low-income families, ultimately contributing to the overall well-being and development of the nation.
References
- World Health Organization (WHO) Kenya – Health Financing and Accessibility in Kenya
- Kenya Ministry of Health – Health Insurance Schemes and National Health Programs
- National Hospital Insurance Fund (NHIF) – Coverage and Benefits for Low-Income Families
- Kenya Health Professionals Association – Community-Based Health Programs in Kenya
- Kenya Medical Association (KMA) – Public-Private Partnerships in Healthcare






