How Kenya’s Foreign Policy is Shaping Relationships with Neighboring Countries

Image Source: TNX Africa
Kenya, a key player in East Africa, has long been recognized for its diplomatic prowess and strategic geopolitical positioning. Over the decades, Kenya’s foreign policy has evolved to address emerging global challenges while fostering robust relationships with its neighbors. From peacebuilding initiatives to cross-border trade partnerships, Kenya has leveraged its foreign policy to become a regional leader. This blog delves into the historical trajectory of Kenya’s foreign policy, the principles guiding it, and its profound influence on diplomatic, economic, and security ties with neighboring countries.
Historical Evolution of Kenya’s Foreign Policy

Image Source: DW
1. Post-Independence Era: 1963–1980s
Upon gaining independence in 1963, Kenya’s foreign policy focused on aligning with Western democracies while promoting Pan-Africanism. The country joined organizations such as the Organization of African Unity (OAU) and the United Nations to advocate for African unity and global cooperation.
- Key Initiative: Kenya’s role in the liberation of southern African nations, including providing logistical support to freedom fighters in Mozambique and Zimbabwe.
- Impact: Kenya’s stance positioned it as a proponent of anti-colonialism and peacebuilding.
2. The Moi Era: 1980s–2000s
During President Daniel arap Moi’s tenure, Kenya emphasized neutrality and non-alignment in regional conflicts. However, internal political instability slightly weakened its diplomatic edge.
- Key Achievement: Hosting peace talks for Somalia and Sudan in the 1990s.
- Challenge: Criticism for insufficient action during the Rwandan Genocide (1994).
3. The Kibaki and Uhuru Eras: 2003–2022
Under Presidents Mwai Kibaki and Uhuru Kenyatta, Kenya’s foreign policy pivoted towards economic diplomacy. The country championed regional integration through the East African Community (EAC) and promoted Kenya as a hub for investment.
- Notable Agreements: Signing of the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) and bilateral pacts with Uganda, Tanzania, and Ethiopia.
- Impact: Growth in trade, infrastructure projects like the LAPSSET Corridor, and energy collaborations.
Key Principles Guiding Kenya’s Foreign Policy

Image Source: Amison-au.org
1. Peace and Security
Kenya is a leading advocate for regional stability, often mediating conflicts and contributing troops to peacekeeping missions.
- Example: Kenya’s role in mediating the Sudan peace talks, leading to the signing of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement (CPA) in 2005.
- Current Impact: Ongoing efforts in Somalia through the African Union Transition Mission in Somalia (ATMIS).
2. Economic Diplomacy
Kenya aims to position itself as a trade and investment hub in East Africa by fostering economic ties with neighbors.
- Initiative: LAPSSET Corridor connecting Kenya to Ethiopia and South Sudan to boost trade.
- Statistics: Kenya exported goods worth over $700 million to Uganda in 2023, showcasing strong bilateral trade.
3. Regional Integration
Kenya actively supports integration within the EAC to promote free movement of people, goods, and services.
- Example: The seamless operation of the EAC Single Customs Territory.
- Impact: Increased cross-border trade, particularly with Uganda, Tanzania, and Rwanda.
Impact of Kenya’s Foreign Policy on Neighboring Countries
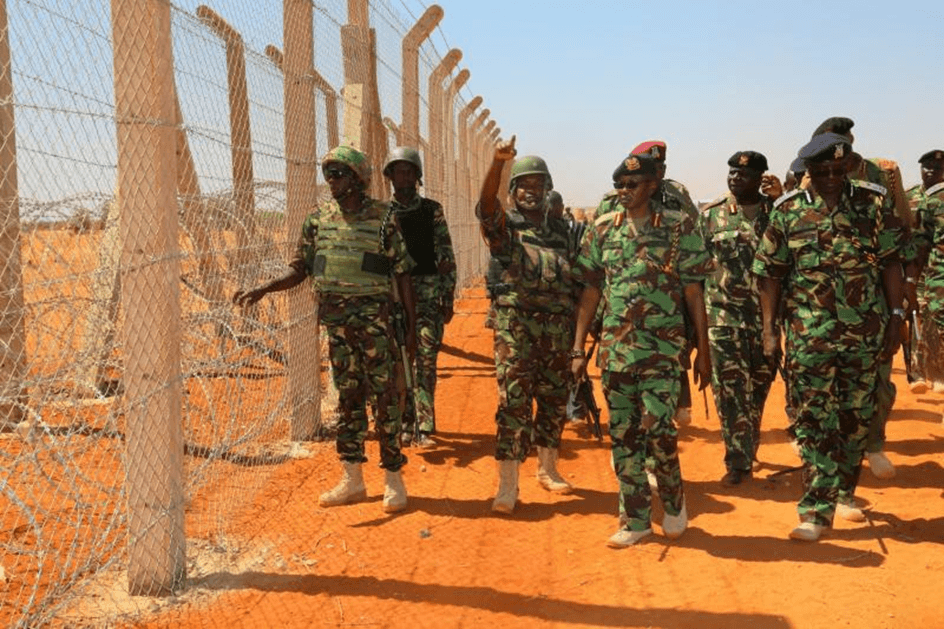

Image Source: The Standard
1. Diplomatic Relations
Kenya’s diplomatic ties are characterized by mutual cooperation and conflict resolution.
- Example: Kenya’s diplomatic efforts in stabilizing South Sudan through IGAD (Intergovernmental Authority on Development).
- Expert Opinion: Dr. Monica Juma, a former Foreign Affairs Cabinet Secretary, emphasizes Kenya’s leadership role in IGAD as pivotal for regional stability.
2. Economic Relations
Trade with Neighbors
Kenya remains a vital trading partner for Uganda, Tanzania, Ethiopia, and Somalia.
- Statistical Insight: The EAC trade volume reached $8.4 billion in 2023, with Kenya being a key contributor.
- Highlight: Kenya’s exports to Ethiopia include agricultural machinery and petroleum products, boosting bilateral trade.
Infrastructure Development
Projects like the Standard Gauge Railway (SGR) and LAPSSET enhance regional connectivity.
- Impact: Faster transportation of goods from Mombasa port to landlocked neighbors.
3. Security Cooperation
Kenya collaborates with neighbors to combat terrorism and cross-border crimes.
- Example: Kenya’s role in Operation Linda Nchi (2011), a military initiative to stabilize Somalia and curb Al-Shabaab activities.
- Impact: Enhanced regional security and reduced terror threats.
Challenges in Kenya’s Foreign Policy Implementation
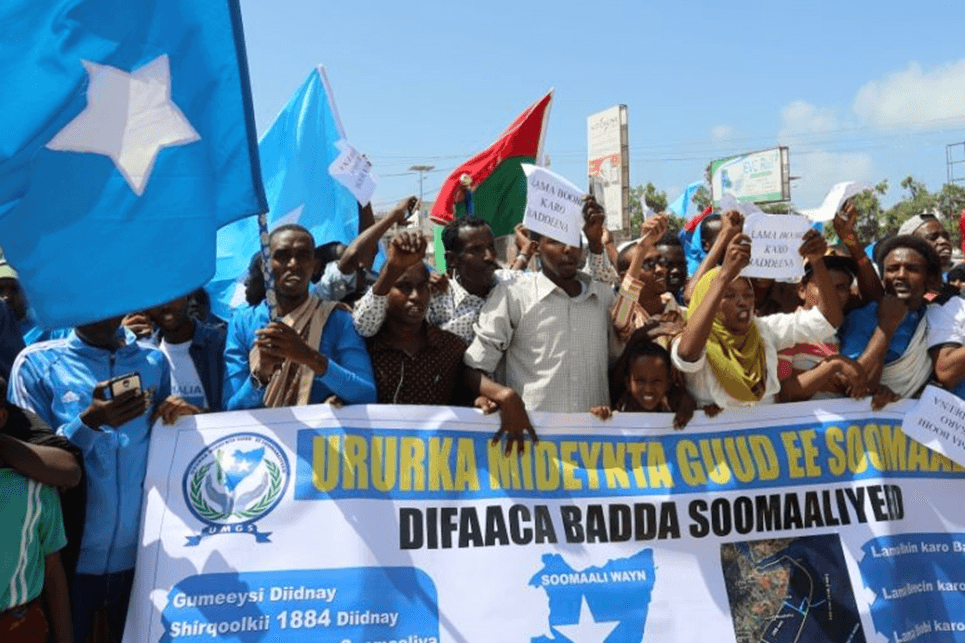

Image Source: AI Jazeera
1. Border Disputes
Kenya has experienced tensions over territorial claims, particularly with Somalia regarding maritime boundaries.
- Current Status: The International Court of Justice (ICJ) ruled in favor of Somalia in 2021, but Kenya contested the decision.
2. Economic Competition
Growing competition with Tanzania has occasionally strained relations, especially in trade and labor laws.
3. Internal Political Dynamics
Domestic challenges, such as election disputes, sometimes affect Kenya’s focus on foreign policy.
Conclusion: Future Implications of Kenya’s Foreign Policy
Kenya’s foreign policy continues to shape the nation’s role as a regional powerhouse. By prioritizing peace, economic growth, and integration, Kenya has cemented its position as a reliable partner in East Africa. However, addressing challenges like border disputes and economic competition is crucial for sustained success.
Key Takeaway:
With strategic planning and robust diplomacy, Kenya can lead East Africa into an era of unparalleled prosperity and stability, setting an example for other nations.








