Kenya’s Power Grid Expansion: The Challenges and Benefits
Introduction: Overview of Kenya’s Current Power Grid and the Importance of Expansion

Source: matsuoutdoorsmanshow
Kenya’s power grid serves as the critical foundation for the country’s economic development, connecting industries, households, and essential services to electricity. Despite commendable progress in expanding electricity access, particularly in rural areas, Kenya’s power infrastructure still faces several obstacles. The demand for electricity continues to grow as the population rises, urbanization accelerates, and new industries emerge. This growth demands a modernized, expanded, and more reliable power grid to meet the needs of a developing nation. The expansion of Kenya’s power grid is not only essential for improving the quality of life of its citizens but also for supporting sustainable economic growth, technological advancement, and the integration of renewable energy sources. This blog delves into the challenges and benefits of expanding Kenya’s power grid, while also drawing lessons from global case studies.
Challenges Facing Kenya’s Power Grid Expansion

Source: Powerline Magzine
Expanding Kenya’s power grid is no small feat, especially given the range of hurdles it must overcome. From infrastructure challenges to complex regulatory environments, the process requires careful planning and significant resources.
Infrastructure and Funding Limitations
A major constraint in the expansion of Kenya’s power grid is the country’s inadequate infrastructure, especially in rural and remote regions. Although the grid has been extended to several urban areas, rural electrification remains a pressing challenge. Establishing new infrastructure like transmission lines, substations, and transformers to reach these underserved areas requires substantial investment. Securing the necessary funding, whether through government sources, international loans, or private partnerships, is a complex process fraught with bureaucratic challenges. Without adequate funding, the expansion of the grid will remain slow and may limit the reach of electricity services.
Regulatory and Policy Challenges
Kenya’s energy sector faces a fragmented regulatory landscape, making it difficult to streamline power grid expansion projects. Although there have been efforts to create clearer policies, inconsistencies and delays in approvals still hinder progress. Additionally, coordination between different stakeholders, such as government agencies, private companies, and local authorities, remains a challenge. Without a robust policy framework that encourages investment and reduces bureaucracy, Kenya will struggle to accelerate the development of its energy infrastructure.
Environmental and Social Impacts
Expanding the power grid also carries significant environmental and social considerations. The construction of power transmission lines and substations can disrupt ecosystems, agricultural land, and even wildlife habitats. In some cases, land acquisition for new infrastructure projects can lead to displacement, with adverse effects on communities. Additionally, concerns about the environmental impact of power grid development—especially in regions with rich biodiversity—must be taken into account to ensure that sustainability remains a priority. Mitigation strategies and community engagement are crucial to balancing development with environmental stewardship.
Benefits of Expanding Kenya’s Power Grid
While the expansion of Kenya’s power grid poses significant challenges, the potential benefits are far-reaching and could transform the country’s energy landscape, improving both economic and social outcomes.
Enhanced Energy Access and Economic Growth
Expanding the power grid ensures that more Kenyans—especially those in rural areas—gain access to reliable electricity. The benefits of electrification extend far beyond lighting homes. Access to electricity empowers businesses, drives industrialization, supports education, and enables healthcare services to function more efficiently. Furthermore, energy access stimulates economic growth by providing the necessary infrastructure for businesses to thrive, which in turn creates more job opportunities and reduces poverty.
Supporting Renewable Energy Integration
Source: Medium
Kenya has made significant strides in harnessing renewable energy sources, including geothermal, wind, and solar power. However, one of the challenges is the efficient integration of these renewable energy sources into the national grid. The expansion of the grid allows for more renewable energy to be absorbed and distributed to meet demand. This shift not only helps reduce Kenya’s dependence on fossil fuels but also contributes to achieving its climate change and energy sustainability goals. A larger grid capacity facilitates greater energy security, while enabling Kenya to fulfill its commitment to greener, more sustainable energy practices.
Job Creation and Development Opportunities
Source: New River Electrical Corporation
The expansion of Kenya’s power grid brings numerous job opportunities to the country. These include both direct jobs in the construction and maintenance of the grid and indirect jobs in sectors like materials supply, transportation, and local services. Additionally, expanding access to electricity opens up new opportunities for entrepreneurship, especially in rural areas, where small businesses can grow thanks to a stable energy supply. The job creation potential of the power grid expansion will contribute significantly to Kenya’s economic development and social stability.
Global Case Studies: Lessons from Similar Power Grid Projects
Kenya can draw valuable lessons from other countries that have faced similar challenges in expanding their power grids. By studying these global case studies, Kenya can adopt strategies that work and avoid pitfalls that others have encountered.
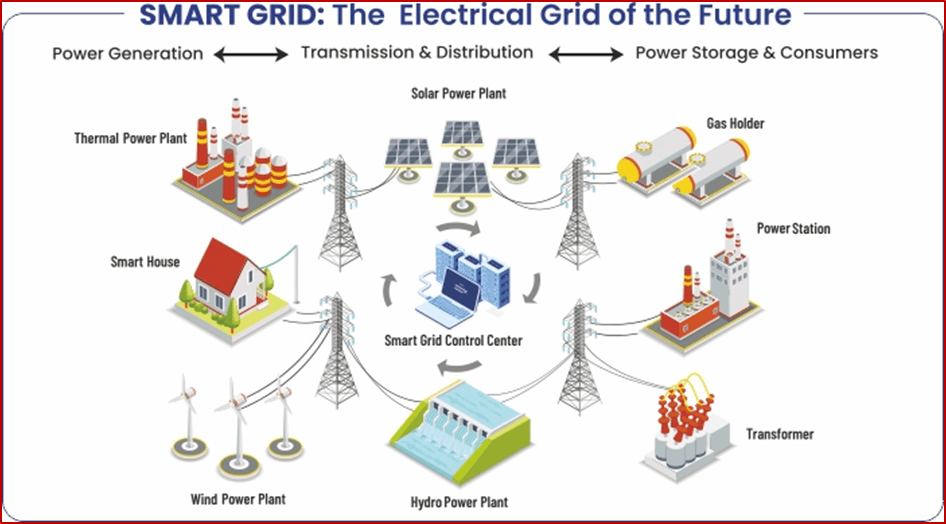
India: Rural Electrification and Smart Grids
Source: Wire & Cable India
India’s approach to rural electrification offers useful insights for Kenya. The government’s flagship program, the Deen Dayal Upadhyaya Gram Jyoti Yojana (DDUGJY), has successfully brought power to millions of rural households. India has also been pioneering the implementation of smart grid technologies, which allow for more efficient distribution and management of energy. Kenya can adopt a similar approach by leveraging technology to optimize grid operations and make power delivery more efficient.
South Africa: Renewable Energy Integration
South Africa has developed a successful renewable energy procurement program known as the Renewable Energy Independent Power Producer Procurement Programme (REIPPPP). Through this program, private investors have contributed to the country’s renewable energy capacity, which has been integrated into the national grid. Kenya can adopt similar public-private partnerships to drive the integration of renewable energy into its grid and ensure long-term sustainability.
Vietnam: Overcoming Policy and Regulatory Challenges
Vietnam has undertaken a significant expansion of its energy infrastructure, overcoming many regulatory and policy-related challenges along the way. Key to its success has been the simplification of its regulatory framework and better coordination among public and private sector stakeholders. Kenya can learn from Vietnam’s experience by focusing on policy reforms that reduce bureaucratic bottlenecks and attract both local and international investments.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways and Future Prospects for Kenya’s Energy Sector

Source: Linkedln
Expanding Kenya’s power grid is a monumental yet necessary task that will shape the country’s future. The challenges—ranging from infrastructure limitations to regulatory hurdles—are significant, but the benefits far outweigh them. By addressing these challenges strategically, Kenya can transform its energy sector into one that supports sustainable growth, enhances economic opportunities, and integrates renewable energy sources effectively. With continued investment, a focus on policy reforms, and adoption of best practices from global case studies, Kenya can overcome obstacles and ensure a bright, electrified future for all its citizens.
References: